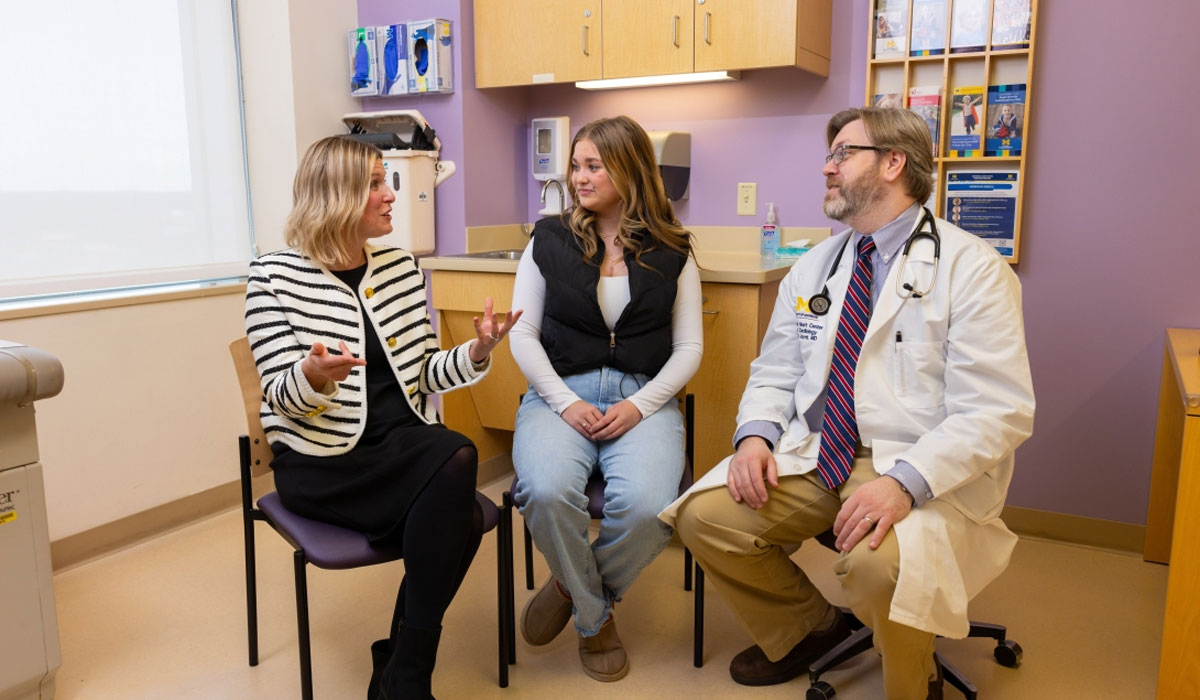
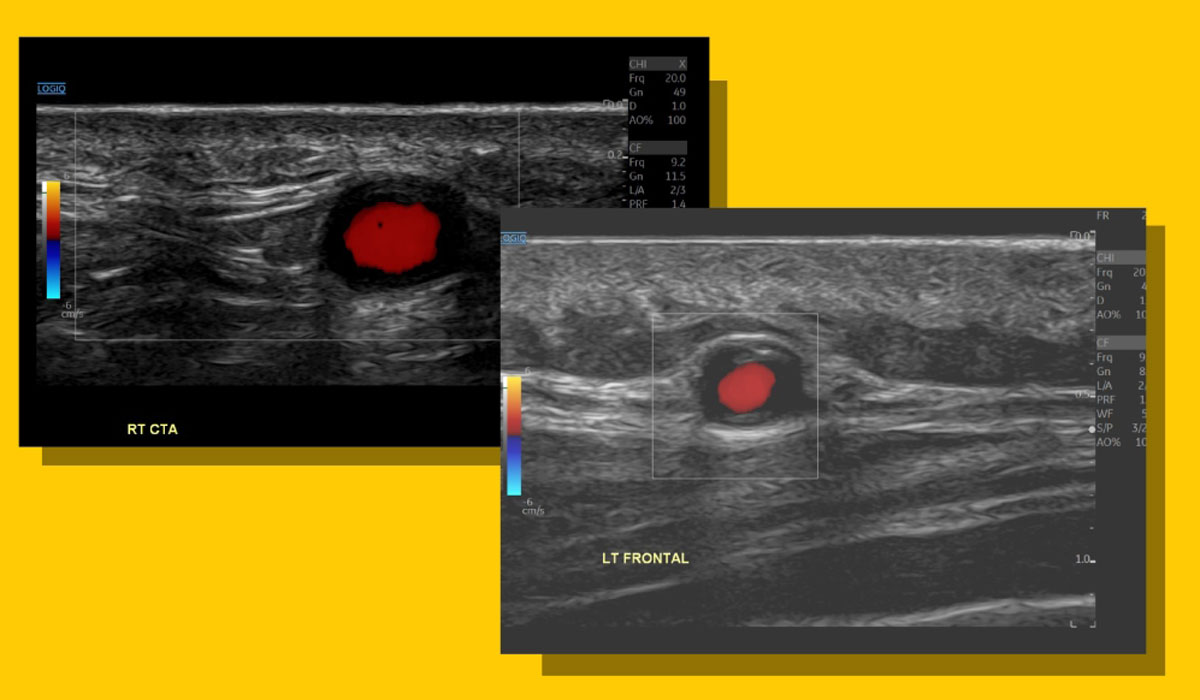
Michigan Medicine is developing a non-invasive ultrasound method to diagnose giant cell arteritis (GCA), a disease that affects people over 50. Led by the U-M Vasculitis Program and Diagnostic Vascular Unit, this new technique could replace traditional biopsies, offering a faster and safer option. It has shown great accuracy and could help doctors start treatment sooner, reducing the risk of serious complications, such as vision loss.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. By using this site, you accept our use of cookies.